Table of Contents
Introduction of Compound Interest Formula
Compound interest is like a secret treasure chest hidden in the world of finance, and it has the power to change your financial destiny. It’s a phenomenon where your money earns interest not only on the initial amount invested but also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. This compounding effect can work for you when you’re saving and investing, or against you when you’re dealing with debt. In this article, we’ll explore the compound interest formula, understand its components, and discuss its practical applications.
The Components of the Compound Interest Formula
The compound interest formula is as follows:
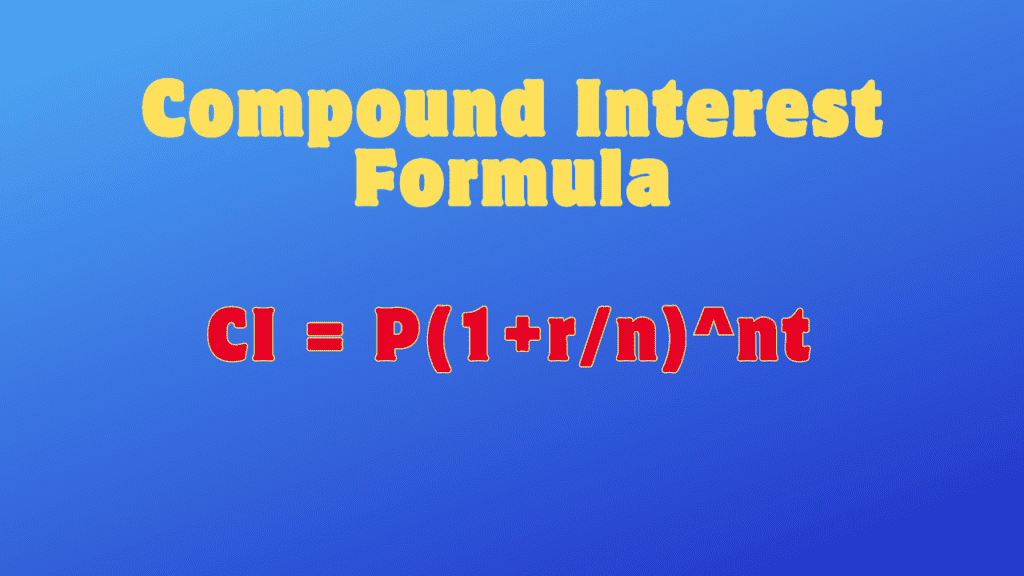
Where:
CI = the future value of the investment or loan, including interest
P = the principal amount (the initial amount of money)
r = the annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal)
n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year
t = the number of years the money is invested or borrowed for
An Example to Calculate Compound Interest
Let’s calculate how the compound interest formula works with a practical example. Imagine you have Rs.1,000 to invest in a savings account with an annual interest rate of 5%. The bank compounds interest quarterly, and you plan to leave the money for 5 years.
In this Question
P = 1000
r = 5% = 0.05
n = compound interest quarterly per year = 12/3 = 4
t = 5 years
Using the compound interest formula:
\[CI = 1000 \times \left(1 + \frac{0.05}{4}\right)^{4 \times 5}\]
\[ CI \approx 1000 \times (1.0125)^{20} \]
\[CI \approx \text{Rs.}1,282.04\]
So, after 5 years, your Rs.1,000 investment will grow to approximately Rs. 1,282.04. You earned Rs.282.04 in interest on top of your initial Rs.1,000
Practical Applications of Compound Interest
Savings and Investments:
Compound interest is a fundamental concept in personal finance. It is used to calculate the growth of savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs, and various types of investments, such as stocks and bonds. Investors use compound interest to estimate the future value of their investments and make informed decisions about where to put their money for optimal growth.
Loans and Debt:
On the other side of the coin, compound interest is also relevant when dealing with loans and debt. When you take out a loan or carry a balance on a credit card, you are essentially borrowing money and accruing interest over time. The compound interest formula is used to calculate the total cost of borrowing and helps borrowers understand how much they will end up paying back.
Mortgages:
Mortgages are one of the most common examples of compound interest in everyday life. When you take out a mortgage to buy a home, your monthly payments include both principal and interest. Over the life of the mortgage, you end up paying back much more than the original loan amount because of the compounding interest. Homebuyers often use mortgage calculators to estimate their total payments over the life of the loan.
Credit Cards:
Credit card companies use compound interest to calculate the interest you owe on your outstanding balance. If you carry a balance on your credit card, the interest compounds daily, leading to rapid growth in the amount you owe if you don’t pay off your balance in full each month.
The Rule of 72: Estimating the Doubling Time:
The Rule of 72 is a handy rule of thumb for estimating how long it will take for an investment to double in value with compound interest. To use this rule, you divide 72 by the annual interest rate. The outcome is like a rough estimate of the time it would take for your investment to become twice as big.
For example, if you have an investment with an annual interest rate of 6%, you can estimate that it will take approximately 12 years (72 ÷ 6) for your investment to double. While this rule is not entirely precise, it provides a quick and easy way to assess the potential growth of your investments.
The Importance of Compound Interest in Financial Planning
Start Early
Time is a critical factor in the power of compound interest. The longer your money is invested, the more significant the impact of compounding. Starting to save and invest early in life can make a substantial difference in your financial well-being.
Consistency Matters
Regular contributions to your investments, like monthly deposits to a retirement account or consistent additions to your savings, can amplify the effects of compounding. Consistency in saving and investing allows you to benefit from compounded growth over time.
Compound Interest and Debt
While compound interest can work in your favor when you’re investing, it can work against you when you have debt. High-interest debts, like credit card balances, can grow rapidly due to compounding. It’s essential to pay off high-interest debts as soon as possible to avoid accumulating excessive interest charges.
Diversification
Compound interest is relevant in various investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Diversifying your investment portfolio can help manage risk while taking advantage of the power of compounding in different areas of the market.
Emergency Fund
Having an emergency fund in a savings account can provide financial security in unexpected situations. The interest earned on your emergency fund will also grow over time, thanks to compound interest.
Final Thoughts
The compound interest formula is a valuable tool that demonstrates the remarkable potential of exponential growth in your finances. Whether you’re an investor seeking to grow your wealth or someone managing debt and striving for financial stability, a solid grasp of compound interest can help you make informed and strategic financial choices. By understanding how compound interest works and the factors that influence it, you can harness its power to achieve your financial goals and build a brighter financial future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, compound interest is a force that can either work for you or against you in your financial journey. Understanding its mechanics and leveraging it wisely can lead to financial prosperity and security. Whether you’re building your savings, investing in the stock market, or managing debt, the concept of compound interest plays a pivotal role in your financial well-being.
FAQs
1. What is compound interest?
Compound interest is the interest calculated on the initial principal amount and the accumulated interest from previous periods. It leads to exponential growth in savings and investments over time.
2. How can I benefit from compound interest?
You can benefit from compound interest by starting to save and invest early, maintaining consistency in contributions, and diversifying your investments for optimal growth.
3. Why is it essential to pay off high-interest debt quickly?
High-interest debts, like credit card balances, can accumulate rapidly due to compound interest. Paying them off quickly helps avoid excessive interest charges.
4. How does compound interest impact mortgages?
Mortgages involve compound interest, meaning you end up paying more than the original loan amount over the life of the loan.
5. What is the Rule of 72, and how is it used?
The Rule of 72 is a rule of thumb to estimate how long it takes for an investment to double in value. You divide 72 by the annual interest rate to get an approximate doubling time.








